Contraceptive Means Including Bith Control Alesse
Contraception (lat. «contraceptio» – exception) is pregnancy prevention by mechanical (condoms, cervical caps, etc.), chemical (e. g., vaginal balls, gramicidin paste) and other antipregnancy means. Some methods (e. g., condoms) help significantly reduce the possibility of HIV infection and prevent other sexually transmitted diseases.
Methods of Contraception
For evaluating contraception method effectiveness there is Pearl Index, showing how many women out of hundred became pregnant using a particular contraceptive method during one year. Despite Pearl Index large rate scatter from different sources (mainly due to the fact what indicators are recorded during researches), this indicator is a good guide to choose a contraceptive method. Without contraception at unprotected sexual intercourse Pearl index is 80-85.
Safety of most contraception methods depends mainly on proper application. Some of them, such as thermal method, requires self-discipline and regulated daily routine.

A woman determines the most favorable time for conception and abstains from sex during these so-called «dangerous days» or uses other contraception means, such as a condom. Coitus interruptus (interrupted sexual intercourse) can also be referred to traditional contraception methods.
Barrier method.
Barrier (mechanical) contraception methods purpose is to prevent sperm from meeting the egg. Currently, male and female condoms are the only contraceptives that prevent sexually transmitted diseases, including HIV-infection, so they can be used also in addition to other (hormonal, chemical) contraceptive methods («safe sex»). At the same together with protection from infections contraceptive effect is increased.
Chemical method.
Chemicals function is to provide a barrier for sperm cells (change cervical mucus or create foam in vagina). They are released in balls, pastes, ointments and pills; applied locally right before sexual intercourse.
Surgical method.
Sterilization and vasectomy – deprivation of reproduction ability by surgery.
Intrauterine devices.
Intrauterine and other devices are placed directly in the uterus; mostly mechanical effect is combined with long-term chemical action. They inhibit sperm cells and reduce an existing period of the egg, but in general have an abortive effect, preventing a zygote from attaching to uterus wall after conception.
Hormonal contraception.
Hormonal drugs act in different ways, depending on their composition. Combined oral contraceptives (COCs) suppress ovulation (i. e. prevent egg maturation and release), moreover condense cervical mucus, thereby making cervix impenetrable for sperm cells, and also change endometrium so that fertilized egg can not attach to it. Acting principal of mini-pill (pills containing only progestin in small amounts), is different – they do not suppress ovulation, but only affect cervical mucus and prevent a fertilized egg from attaching to the uterus wall.
It should be noted that hormonal contraceptives have a number of disadvantages:
- they do not protect from sexually transmitted diseases;
- long reception of these contraceptives can increase the risk of several diseases: candidiasis, venous thrombosis / venous thromboembolism, heart attack, blood stroke, osteoporosis, anemia, including cancer (breast cancer, cervical adenocarcinoma, liver cancer;
- birth control pills administration should be long-term and permanent, which requires a lot of attention and expenses; each missed pill increases pregnancy risk;
- in some cases, there are side effects, such as sickliness, dizziness, vomiting, headaches, breast tenderness, weight gain.
Contraceptives Contraindications
There are two groups of contraindications for COC prescription – absolute and relative. Absolute contraindications correspond to the IV category of contraceptive methods acceptability according to WHO recommendations, relative contraindications correspond to the III category. Absolute contraindications forbid COCs intake, in any case, relative – allow with reservations, for example, possible to use only low-dose short-term preparations.
Relative:
- moderately severe arterial hypertension; phlebeurysm; severe headaches or migraines, caused by COCs; mental diseases accompanied by depression, epilepsy; otosclerosis;
- previous breast cancer (with no manifestation for 5 years);
- elective surgery (4 weeks before surgery);
- sickle-cell anaemia;
- acute mononucleosis;
- smoking more than 15 cigarettes a day being over 35 years old.
Absolute:
- severe cardiovascular system diseases and cerebral vessels (CAD, myocardial infarction in anamnesis, cerebrovascular accident, cerebral ischemia);
- thrombophlebitis currently or in the past;
- severe arterial hypertension;
- severe liver diseases currently or in the past, if liver function indicators are not returned to normal;
- migraines with focal neurological signs;
- breast and genitals malignoma or their suspected presence;
- vaginal bleeding for unspecified cause;
- porphyria;
- prominent hyperlipoproteinemia;
- severe itching or herpes caused by pregnancy or steroidal agents;
- diabetes at presence retinopathies;
- pregnancy;
- lactation period.
Alesse Birth Control
Nowadays Alesse Birth Control is the most popular and effective contraceptive, that almost doesn’t cause side effects. 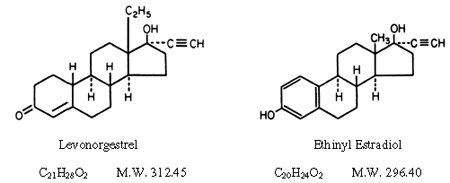
Alesse generic name is ethinyl estradiol and levonorgestrel – a combined drug that contains female hormones for ovulation prevention (egg release from ovarium). The preparation also causes changes in cervical mucus and endometrium, preventing sperm cells from reaching uterus fertilized egg from attaching to the uterus wall.
Alesse Birth Control is used for contraception to prevent pregnancy; may also be used for purposes not listed in its medication guide.
The medication acts by suppressing gonadotropic hormones. Although initial action mechanism was inhibition of ovulation, other alterations include changes in cervical mucus (which increases the difficulty for a sperm cell to entry uterus) and endometrium (which reduce the possibility of implantation).